Human migration has been a constant throughout history. In recent decades, the scale and complexity of global migration have increased significantly. Understanding these trends is crucial, as they have profound economic implications for countries worldwide.
Global migration encompasses the movement of individuals from one country to another, driven by various factors such as economic opportunities, political instability, environmental changes, and family reunification. According to the International Organization for Migration, there were approximately 281 million international migrants in 2020, accounting for 3.6% of the global population.
This article aims to explore recent trends in global migration and analyze their economic impacts on host countries. By examining current data and case studies, we will shed light on how migration shapes labor markets, public finances, and overall economic growth.
Key Points to Be Addressed
- Current Migration Statistics: An overview of the latest data on international migration flows and stocks.
- Economic Contributions of Migrants: Discussion on how migrants influence labor markets, innovation, and fiscal balances in host countries.
- Challenges and Policy Responses: Examination of the challenges host countries face due to migration and the policies implemented to address them.
By delving into these areas, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted relationship between global migration and economic development.
Current Global Migration Trends
Global migration patterns have evolved significantly in recent years, influenced by various economic, social, political, and environmental factors. Understanding these trends is essential for policymakers and stakeholders to address the challenges and opportunities arising from human mobility.
Increase in International Migrants
- Rising Numbers: The number of international migrants has seen a substantial increase over the past decades. In 2020, there were approximately 281 million international migrants globally, accounting for 3.6% of the world’s population.
- Recent Surge: In 2023, migration to OECD countries reached a record high, with around 6.5 million people moving to these nations – a 10% increase from the previous year. This surge was notably significant in the United Kingdom, which, for the first time, surpassed the United States as the largest recipient of immigrants, driven by demand in sectors like healthcare.
Major Destination Regions and Countries
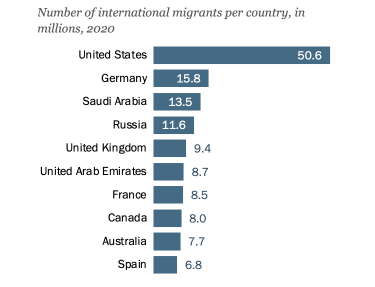
Number of international migrants, 2020
- Top Host Countries: High-income countries continue to be primary destinations for migrants seeking better economic opportunities. The United States, Germany, and Saudi Arabia are among the top destinations, attracting migrants due to robust economies and labor market demands.
- Emerging Destinations: Countries like Canada, Australia, and the United Kingdom have also seen significant increases in migrant populations, driven by policies favoring skilled migration and educational opportunities.
Demographic Shifts in Migrant Populations
- Labor Market Needs: Labor shortages and aging populations in many developed countries have led to increased labor migration, particularly in sectors such as healthcare and technology.
- Forced Displacement: By the end of 2023, the number of forcibly displaced people worldwide reached an estimated 117.3 million, driven by conflicts, persecution, and human rights violations.
- Environmental Factors: Climate change has emerged as a significant driver of migration, with extreme weather events and environmental degradation forcing individuals to relocate. Regions experiencing severe droughts, rising sea levels, and natural disasters are witnessing increased displacement.
These evolving migration trends underscore the need for comprehensive policies that address the root causes of migration while leveraging the potential benefits of human mobility for both origin and destination countries.
Economic Implications for Host Countries
Migration significantly influences the economies of host countries, affecting labor markets, public finances, and innovation. Understanding these impacts is crucial for policymakers to harness the benefits while addressing potential challenges.
Labor Market Contributions
Addressing Labor Shortages
Migrants often fill essential roles in sectors experiencing labor shortages, such as healthcare, agriculture, and technology. For instance, in the United Kingdom, increased migration has been pivotal in supporting the National Health Service and other critical industries.
Wage and Employment Effects
Research indicates that immigration generally has a small but positive impact on the average wages of native workers. While there may be slight wage reductions in specific low-skilled sectors, the overall effect tends to be neutral or positive.
Fiscal Impact
Tax Contributions vs. Public Service Usage
Studies show that immigrants contribute more in taxes and social contributions than they receive in benefits. This positive fiscal impact is particularly evident among labor migrants who are actively employed.
Public Spending
The presence of migrants can lead to increased government spending on services such as education and healthcare. However, the tax contributions from immigrants often offset these costs, resulting in a net fiscal benefit.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Driving Innovation
Immigrants play a crucial role in fostering innovation within host countries. They contribute to technological progress and the development of new ideas, enhancing overall productivity.
Entrepreneurial Activities
Many migrants establish businesses, creating jobs and stimulating economic growth. Their entrepreneurial endeavors diversify the market and introduce new products and services.
In summary, migration contributes positively to the economic landscape of host countries by filling labor gaps, bolstering public finances, and driving innovation. While challenges exist, the overall economic implications are beneficial when effectively managed.
Challenges Faced by Host Countries
While migration offers numerous economic benefits, host countries often encounter significant challenges in managing the influx of migrants. These challenges encompass social integration issues, policy and infrastructure strains, and political tensions.
Social Integration
- Cultural Integration and Social Cohesion: Integrating migrants into the social fabric of host countries can be complex. Differences in language, customs, and cultural practices may lead to misunderstandings and social friction. For instance, the arrival of large numbers of refugees in Europe during the 2015 migrant crisis highlighted the difficulties in achieving social cohesion.
- Public Perception and Attitudes: Public attitudes towards migrants significantly influence integration outcomes. Negative perceptions can lead to discrimination and social exclusion, hindering migrants’ ability to contribute effectively to society. Recent anti-immigration sentiments in various European countries have underscored the importance of addressing public concerns to foster a more inclusive environment.
Policy and Infrastructure Strain
- Pressure on Public Services: An influx of migrants can strain public services such as housing, healthcare, and education. For example, Turkey, hosting over 3.5 million Syrian refugees, has faced significant challenges in providing adequate services, leading to increased competition for resources and social tensions.
- Policy Responses and Legal Challenges: Developing effective migration policies is a complex task. The European Union, for instance, has grappled with creating a unified asylum system, balancing the need for security with humanitarian obligations. Recent proposals to reform asylum policies, including plans to deport failed asylum seekers, have sparked legal and ethical debates.
Political Tensions
Rise of Populism and Nationalism: The challenges associated with migration have fueled the rise of populist and nationalist movements in several countries. These movements often advocate for stricter immigration controls and can disrupt political stability. The anti-immigration mood sweeping across EU capitals exemplifies this trend, posing threats to the bloc’s unity and its new asylum strategy.
Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that balances the economic benefits of migration with the need for social cohesion and political stability. Policies should focus on promoting effective integration programs, investing in public infrastructure, and fostering public dialogue to mitigate negative perceptions. By adopting comprehensive strategies, host countries can turn migration challenges into opportunities for growth and cultural enrichment.
The Future of Social Finance in Migrant Integration
As global migration trends continue to evolve, the role of social finance in supporting migrant integration is poised to become increasingly significant. Emerging trends and innovative approaches offer promising avenues for enhancing the effectiveness of these initiatives.
Digital Financial Inclusion
The advancement of digital finance presents new opportunities for integrating migrants into the financial system. Innovations such as mobile banking and digital remittances can provide migrants with accessible financial services, facilitating economic participation and stability. For example, digital finance has been shown to promote migrant workers’ integration into urban life by improving their financial inclusion and resilience.
Social Impact Bonds
Social Impact Bonds (SIBs) are emerging as a novel mechanism to fund migrant integration programs. In this model, private investors provide upfront capital for social initiatives and receive returns based on the achievement of predefined outcomes. This approach has the potential to attract new funding sources and foster innovative solutions for migrant integration challenges.
Community-Driven Social Enterprises
There is a growing recognition of the importance of community-driven social enterprises in supporting migrant integration. These enterprises, often led by migrants themselves, address specific community needs while providing employment and fostering social cohesion. Supporting such initiatives through social finance can amplify their impact and sustainability.
Author’s Perspective
The future of social finance in migrant integration lies in embracing innovation and fostering collaboration among stakeholders. By leveraging digital technologies, exploring new financial instruments like SIBs, and empowering community-driven enterprises, we can create more effective and sustainable integration pathways. It is imperative to remain adaptable and responsive to the evolving needs of migrants to ensure that social finance initiatives continue to facilitate successful integration in the years to come.
Conclusion
Global migration presents both opportunities and challenges for host countries. While migrants contribute significantly to economic growth, labor market dynamism, and cultural diversity, their integration requires thoughtful policies and supportive frameworks. Social finance has emerged as a powerful tool in this regard, providing innovative solutions to facilitate the economic and social inclusion of migrants.
By examining current migration trends, understanding the economic implications, addressing integration challenges, and exploring successful case studies, we gain valuable insights into the multifaceted relationship between migration and development. Looking ahead, embracing innovative social finance models and fostering collaborative efforts among governments, private sector, and civil society will be crucial in harnessing the full potential of migration for inclusive and sustainable growth.
In conclusion, while the path to effective migrant integration is complex, the strategic application of social finance offers promising avenues to create resilient and cohesive societies that benefit all members.






